Easy Way To Delete PPA on Linux!
 |
| Image by Pixabay |
Personal Package Archive (PPA) is a repository that can be created by individuals for certain purposes, such as sharing an application's repository with other users globally. PPA makes it easy for many users to install or update an application.
But sometimes, a PPA can be useless when the creator has deleted the repository. So, when we enter the PPA address that the repository has been deleted, it will cause an error when updating on Linux, because the URL is not found. For this reason, the non-functioning PPA is better removed.
How to delete PPA on Linux?
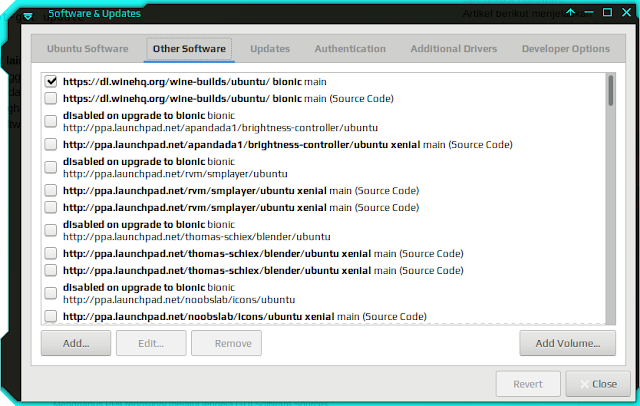
The method is quite easy. If you use Ubuntu or its derivative, you can delete PPA via GUI mode by opening Software & Updates (Software Sources) -> Select the Other Software menu, and please search for PPA in the list, as shown below:
You can search for it, by typing the keywords from the PPA that you want to delete, to speed up the search, after that you have a PPA that has not been used.
The second is using Terminal. This method can be applied to various Linux distributions. But before, you can see a list of registered PPAs using this command:
sudo ls /etc/apt/sources.list.d
To delete it please type the command below:
sudo rm -i /etc/apt/sources.list.d/ppa_name.list -> With prompt before every removal
sudo rm /etc/apt/sources.list.d/ppa_name.list -> without prompt before every removal
On ppa_name.list , please write the name of the PPA that you want to delete. Actually, you can also see the PPA list in the sources.list.d directory using File Manager like this:
Removing PPA is part of clearing errors when there is a ppa address that is not active or cannot be found. Even though the PPA an application you delete, the application installed using the PPA will not be deleted, unless you uninstall the application.
But, if a PPA from the application installed on your computer is inactive, it means you also cannot update the application, and may need to find a new PPA that is still active and provide PPA for updates.